Use Javascript to Fix 12 Common Browser problem
We advocate using CSS whenever possible, and we often successed. Modern browsers have very good support for CSS — it’s certainly good enough for you to use CSS to control layout and presentation. Sometimes however, certain page elements will appear differently in different browsers.
Don’t worry too much if you don’t know the reason why, play around with the CSS rules and check out this post: Using CSS to Fix Anything: 20+ Common Bugs and Fixes as well.
If that doesn’t work, you can fix it up with one of the 12 javascript solutions listed below and your Web pages should look great across all browsers!
In this article, we’ll demystify 12 javascript solutions for the most common CSS issues that you’ll encounter when building web applications.
You might be interested to check other CSS related posts.
- Using CSS to Do Anything: 50+ Creative Examples and Tutorials
- Using CSS to Fix Anything: 20+ Common Bugs and Fixes
1. Setting Equal Heights
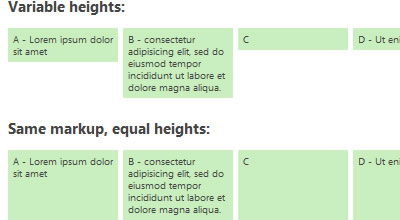
Creating the visual effect of equal-height columns or content boxes has been a challenge ever since we abandoned table-based layouts.
1.1 Setting Equal Heights with jQuery
This jQuery plugin “equalize” the heights of boxes within the same container and create a tidy grid — with little overhead. From a usability and performance standpoint to use a simple JavaScript workaround: equalHeights() function determines the heights of all sibling elements in a container, and then sets each element’s minimum height to that of the tallest element.
How it works
equalHeights() loops through the top-level child nodes of a specified element and sets their min-height values to that of the tallest.
- Demo can be found here.
1.2 Equal height columns with jQuery
Another jQuery plugin “equalize” the heights of boxes.
$("#col1, #col2").equalizeCols();
Will equalize the columns as expected
$("#col1, #col2").equalizeCols("p,p");
Will equalize the columns and add the extra space after the p tag in #col1 or #col2 (whichever is shorter).
2. IE6 PNG Alpha Transperancy support
IE versions below 6 do not support png transparency. With the use of hacks, support has been available in Internet Explorer 5.5 and 6, but the hacks are non-ideal and have been tricky to use. Lets take a look at what we can do to support IE6 users whilst taking full advantage of transparency for the majority of a site’s visitors.
2.1 Force IE6 To Support Alpha Transparency
IE7 is a JavaScript library created by Dean Edwards to force MSIE(IE6, IE5) behave like a standards-compliant browser. It fixes many CSS issues and makes transparent PNG work correctly under IE5 and IE6. It also allows for advanced CSS selectors.
2.2. iFixPng improved

Fix problems with PNG images in IE6 and below, works for both img-elements and css-background-images. This plugin is an improvement to the original iFixPng plugin. Features include: The image or element with a background image doesn’t have to be visible, background-position is now supported, including an IE absolute position fix. (bottom: -1px || bottom: 0px)
3. Changing CSS Classes in JavaScript
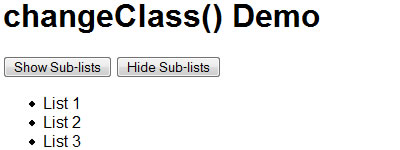
Here is a handy JavaScript function that changes any element of class oldClass to newClass in the current document. This is especially useful for changing styles on the fly using CSS classes instead of hard-coded style values.
function changeClass(oldClass, newClass) {
var elements = document.getElementsByTagName("*");
for( i = 0; i < classname ="=" classname =" newClass;">
4. Browser selectors in CSS
What if you could just type a special selector, where you could write some javascript that sets a class name on, say, the element based on the name of the current browser.

4.1 CSS Browser
This is a very small javascript with just one line and less than 1kb which empower CSS selectors. It gives you the ability to write specific CSS code for each operating system and each browser. You could write some javascript that sets a class name on, say, the element based on the current browser.
jQuery browser selectors
Here is another solution on how to do these browser selectors so easily with jQuery, all you have to do is include the jQuery file, and the following piece of code:
$(document).ready(function(){
$('html').addClass($.browser);
});
Now you can preprend your styles with .msie, .mozilla, .opera, .safari or .other depending on the targeted browser.
- Demo can be found here.
5. min-/max- height & width support
Looking for CSS min-width, min-height, max-width, max-height, border-*-width, margin, and padding properties, here are some good jQuery fixes.
5.1 jQMinMax
This is a jQuery plugin that adds support for min-width, max-width, min-height and max-height where they are not natively supported.
5.2 JSizes
This small jQuery plugin adds support for the CSS min-width, min-height, max-width, max-height, border-*-width, margin, and padding properties. Additionally it has one method for determining whether an element is visible. Because all the size methods return numbers, it is safe to use them in calculating DOM element dimensions.
The example below shows that chaining can be used on methods that do not return values.
jQuery(function($) {
var myDiv = $('#myDiv');
// set margin-top to 100px and margin-bottom to 10em
myDiv.margin({top: 100, bottom: '10em'});
// displays the size of the top border in pixels
alert(myDiv.border().top);
// displays true if the element is visible, false otherwise
alert(myDiv.isVisible());
// set padding-right to 10px and margin-left to 15px using chaining
myDiv.padding({right: 10}).margin({left: 15});
});
6. Center Elements Vertically / Horizontally
You might have come across this problem before : centering elements vertically or horizontally. Vertical centering is rather difficult in CSS, especially if you aim to support all major web browsers. Fortunately, there are solutions that work, one solution takes the value for the left and right marginsfrom the height and width values, divided by two.

6.1 Center element plugin
This plugin center any element in page, horizontal and vertical using the css minus margin method.
$("element").center(); //vertical and horizontal
$("element").center({
horizontal: false // only vertical
});
6.2 How Can I Vertically Center An Element?
In this video tutorial, Jeffrey Jordan Way will show you how you can vertically center an image in your browser by combining CSS with jQuery’s power.
7. Display Q tags in Internet Explorer
Quotation marks are supposed to render with use of the Q tag but not with use of the blockquote tag. However, IE/Win does not render these quotation marks, and because of this, most web authors choose not to use the Q tag.
7.1 QinIE
When you add this script to the head of your document to automatically sweep the page for Q tags in IE and display them properly (including nested quotes). When (if) IE supports Q tags in the future, this will have to be updated with a browser version check.
- Download source file here
8. Increase the size of click targets and get more call-to-action conversions
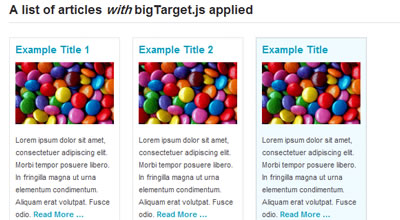
Say goodbye to boring ‘Read More…’ links by turning your entire content block into a clickable target!
- Download source file here
9. Lazy loader
Lazy loader is a jQuery plugin written in JavaScript. It delays loading of images in (long) web pages. Images outside of viewport (visible part of web page) wont be loaded before user scrolls to them. This is opposite of image preloading.
10. bgiframe
Helps ease the pain when having to deal with IE z-index issues.
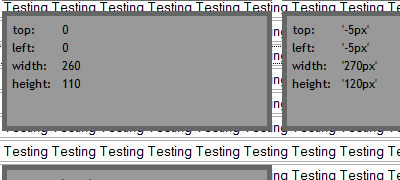
11. ieFixButtons
ieFixButtons is a jQuery plugin that fixes the buggy behavior of the <button> element in Internet Explorer 6 and 7.
12. Fix Overflow
Fixes the horizontal overflow in IE. In particular, IE will place the scroll bar inside the overflowing element, and if the element is only one line, the scroll bar will cover the line. This plugin will adjust the padding to fix the issue.
Labels: Design, Web Design, web usability, website usability




0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Subscribe to Post Comments [Atom]
<< Home